Variable Capital Company (VCC)
A Variable Capital Company (VCC) is a new investment fund corporate structure established under the Variable Capital Companies Act, which came into effect on January 14, 2020. The VCC complements the existing suite of investment fund structures in Singapore.
The VCC Act and its subsidiary legislation are administered by the Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA). All VCCs must be managed by an approved fund manager. The anti-money laundering and countering the financing of terrorism obligations of the VCCs will be overseen by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS).
Application Requirements
- There must be a licensed or regulated fund manager based in Singapore.
- The registered office must be located in Singapore, and a resident company secretary must be appointed.
- For unauthorised schemes, there must be at least one Singapore resident director.
- The company audit must be conducted by a Singaporean auditor.
- The requirements of the current Securities and Futures Act for investment funds must be met.
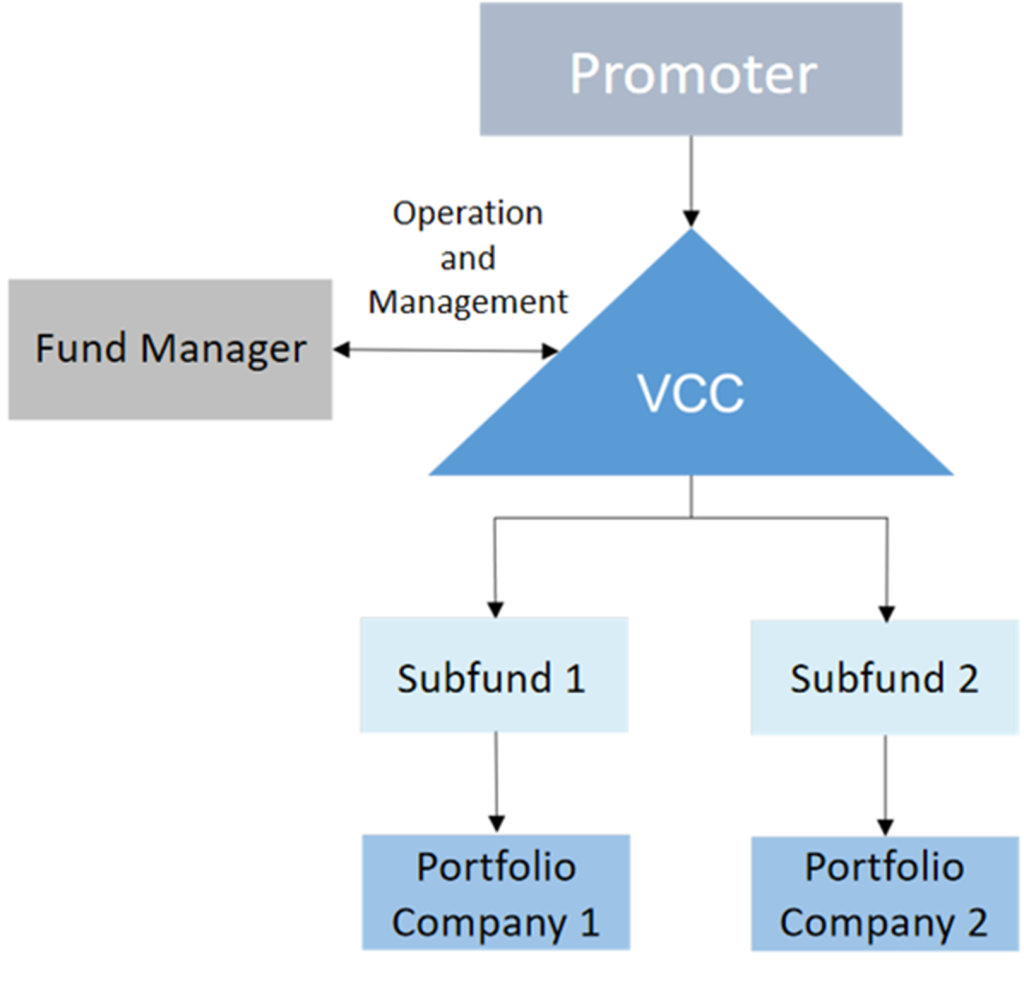
Key Features of VCC
01
VCC has a variable capital structure, allowing for the flexible issuance and redemption of its shares. It can also distribute dividends from its capital, enabling fund managers to fulfil dividend payment obligations flexibly.
02
A VCC can be set up as a standalone fund or as an umbrella fund with two or more sub-funds, each holding an independent portfolio of assets and liabilities. For fund managers structuring funds as umbrella VCCs, using service providers for both the umbrella and its sub-funds could enhance cost efficiency.
03
VCCs can be used for both open-ended and closed-ended fund strategies.
04
Fund managers can merge new VCCs by transferring registrations to Singapore or re-register their existing overseas investment funds with a similar structure as VCCs.
05
VCCs must maintain a register of shareholders, which does not need to be publicly accessible. However, for regulatory, supervisory, and enforcement purposes, the register must be disclosed to public authorities as required.
Combination of VCC and Multi-Family Office (MFO):
- Under the umbrella VCC structure, the liability assets of each sub-fund are mutually separated.
- VCC can be established as an independent entity or as an umbrella VCC with sub-funds. In the umbrella VCC, its sub-funds operate as separate units.
- Multiple family offices can be established under the VCC structure.
- The family office under the VCC structure has the functionalities of both 13O and 13U, as well as additional functions not available in a regular family office.
- An investment in VCC's sub-funds typically requires 10 million SGD, with a requirement to disclose the source of wealth (KYC) but without the need to queue with MAS.
- Appointed by the MFO to oversee their invested sub-funds, one can apply for an Employment Pass (EP).
- Family members can apply for dependent passes, and children can study in Singapore.
- Multiple families can share one MFO+VCC, investing in separate sub-funds while maintaining confidentiality and independence among each other.
Advantages of VCC and Multi-Family Office (MFO):
- No need for the high threshold of 20 million SGD.
- Significantly reduced private banking account opening time for sub-funds.
- No need to queue with MAS for tax incentives in Singapore, while still enjoying the tax exemptions under 13O/13U (applied by the licensed company).
- Multiple families can share one licensed VCC fund structure.
- Reliable investment products with flexible options.
VCC Architecture and Process
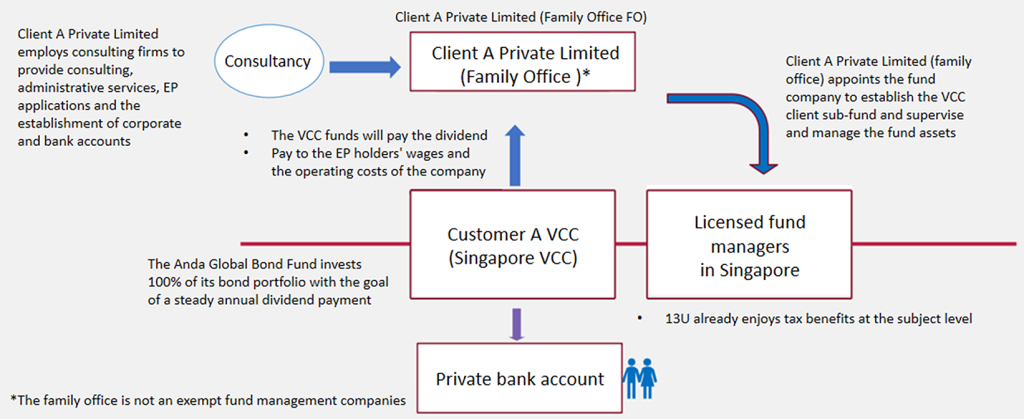
Family Office and VCC Sub-Fund Timeline
01
First Month
Client signs an investment advisory agreement with ATC (deciding investment structure; registering and opening a corporate bank account; gathering important information). Client signs an investment management agreement (establishing VCC sub-fund; gathering necessary information).
02
Within 3 to 6 Months
Processing of Employment Pass (completed within 1-4 weeks) and private banking account opening for the sub-fund.
03
Operation
Once the private banking account is set up, the client's family office begins operating by subscribing to its own sub-fund. (Compared to a traditional family office project cycle of 9-12 months, the VCC structure significantly reduces the time taken.)
Project Advantages

Improve Operational and Tax Efficiency

No Need for Public Financial Reports

Flexible Distribution and Capital Reduction

No Requirement for Public Disclosure of Shareholders Register

